FEATURES
Could AI text alerts help save snow leopards from extinction?
Published
2 months agoon
By
editor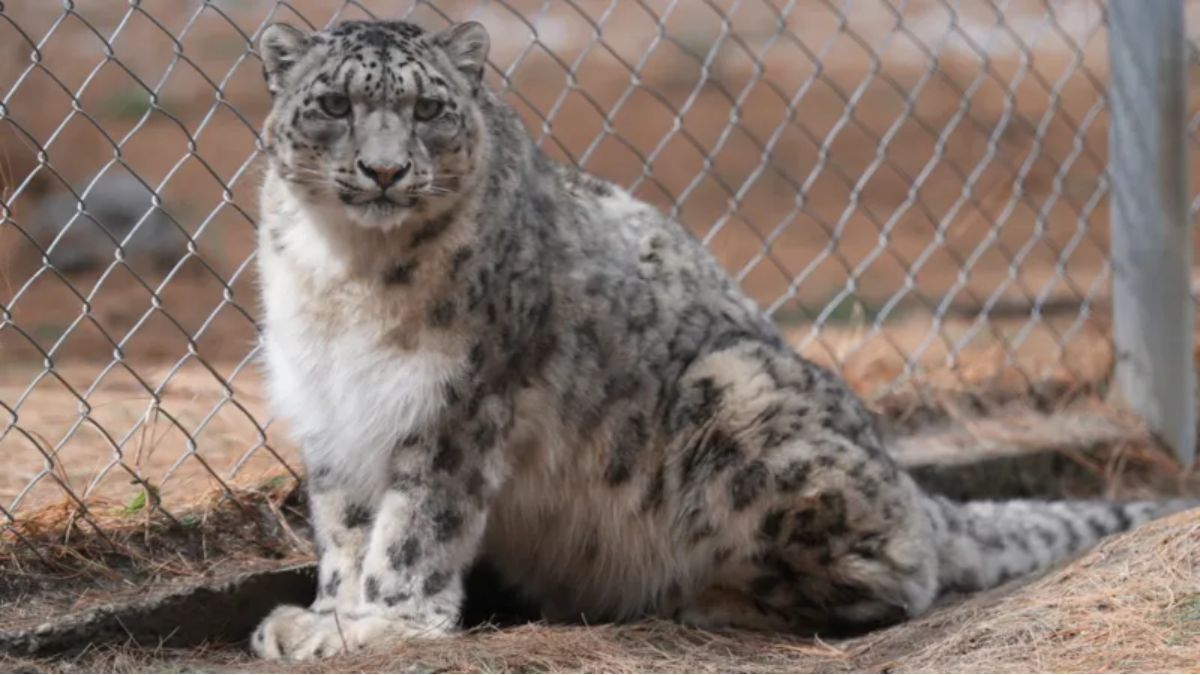
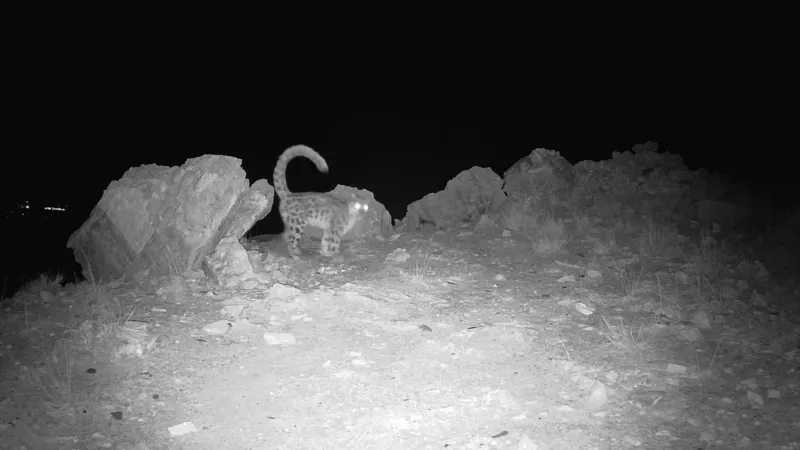
Lovely is one of between 4,000 and 6,000 snow leopards on the planet
Snow leopards cannot growl. So when we step towards one of these fierce predators, she’s purring.
“Lovely,” as she’s called, was orphaned and rescued 12 years ago in Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan.
After years of relying on staff to feed her, she does not know how to hunt in the wild – and cannot be set free.
“If we release her, she would just go attack a farmer’s sheep and get killed,” Lovely’s caretaker, Tehzeeb Hussain, tells us.
Despite laws protecting them, between 221 to 450 snow leopards are killed each year, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) says, which has contributed to a 20% decline in the global population over the past two decades.
More than half of these deaths were in retaliation for the loss of livestock.
Now, scientists estimate that just 4,000 to 6,000 snow leopards are left in the wild – with roughly 300 of these in Pakistan, the third-largest population in the world.
To try and reverse these worrying trends, the WWF – with the help of Pakistan’s Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS) – has developed cameras powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
Their aim is to detect a snow leopard’s presence and warn villagers via text message to move their livestock to safety.
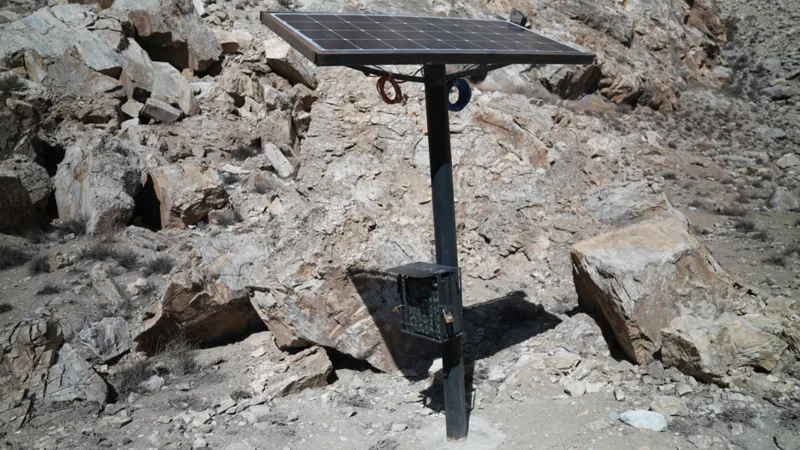

The cameras operate using lithium batteries and solar panels
Tall, with a solar panel mounted on top, the cameras are positioned high among barren and rugged mountains at nearly 3,000m (9,843ft).
“Snow leopard territory,” says Asif Iqbal, a conservationist from WWF Pakistan. He walks us a few more steps and points to tracks on the ground: “These are pretty new.”
Asif hopes this means the camera has recorded more evidence that the AI software – which allows it to differentiate between humans, other animals and snow leopards – is working.
Trial and error
The WWF is currently testing 10 cameras, deployed across three villages in Gilgit-Baltistan. It has taken three years to train the AI model to detect these categories with impressive – if not perfect – accuracy.
Once we’re back down the mountain, Asif pulls up his computer and shows me a dashboard. There I am, in a series of GIFs. It correctly detects I’m a human. But as we scroll down the list, I come up again, and this time I’m listed as both a human and an animal. I’m wearing a thick white fleece, so I forgive the programme.
Then, Asif shows me the money shot. It’s a snow leopard, recorded a few nights prior, in night-vision. He pulls up another one from the week before. It’s a snow leopard raising its tail against a nearby rock. “It’s a mother leopard, looks like she’s marking her territory,” Asif says.
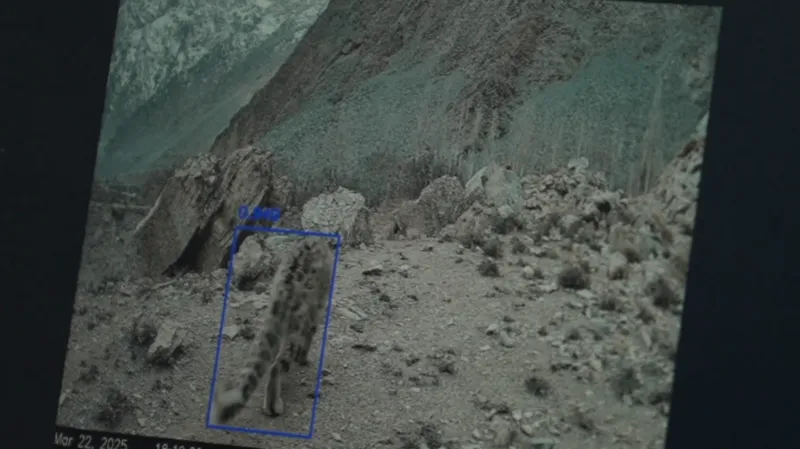

The cameras have been developed to detect a snow leopard’s presence and then warn villagers to move their livestock to safety
Setting up the cameras in rocky, high-altitude areas took a lot of trial and error. The WWF went through several types of batteries until it found one that could withstand the harsh winters. A specific paint was chosen to avoid reflecting light as animals pass by.
If the cellular service fails in the mountains, the device continues recording and capturing data locally. But the team has had to accept there are some problems they simply cannot solve.
While the camera lens is protected by a metallic box, they’ve had to replace solar panels damaged by landslides.
Doubt in the community
It is not just the technology that has caused problems. Getting the local community’s buy-in has also been a challenge. At first, some were suspicious and doubted whether the project could help them or the snow leopards.
“We noticed some of the wires had been cut,” Asif says. “People had thrown blankets over the cameras.”
The team also had to be mindful of the local culture and the emphasis on women’s privacy. Cameras had to be moved because women were walking by too often.
Some villages still have yet to sign consent and privacy forms, which means the technology cannot be rolled out in their area just yet. The WWF wants a binding promise that local farmers will not give poachers access to the footage.
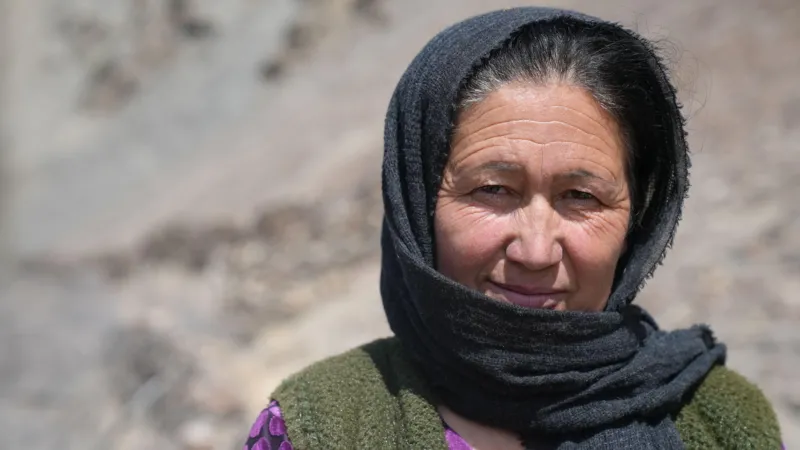

Sitara says a snow leopard killed her sheep while they were grazing
Sitara lost all six of her sheep in January. She says she had taken them to graze on land above her home but that a snow leopard attacked them.
“It was three to four years of hard work raising those animals, and it all ended in one day,” she says.
The loss of her livelihood left her bedridden for several days. When asked if she is hopeful the AI cameras could help in the future, she replies: “My phone barely gets any service during the day, how can a text help?”
At a gathering of village elders, leaders of the Khyber village explain how attitudes have changed over the years, and that a growing proportion of their village understands the importance of snow leopards and their impact on the ecosystem.

According to the WWF, snow leopards hunt ibex and blue sheep, which stops these animals from overgrazing and helps to preserve grasslands so villagers can feed their livestock.
But not all are convinced. One local farmer questions the benefits of the animals.
“We used to have 40 to 50 sheep, now we’ve only got four or five, and the reason is the threat from snow leopards and from ibex eating the grass,” he says.
Climate change also has a part to play in why some feel threatened by snow leopards. Scientists say warming temperatures have led villagers to move their crops and livestock to higher areas in the mountains, encroaching on snow leopards’ own habitat, making livestock more of a target.
Whether the villagers are convinced by the conservation message or not, the WWF tells us legal penalties have served as a strong deterrent in recent years. Three men were jailed in 2020 after killing a snow leopard in Hoper valley, about a two-hour drive from Khyber. One of them had posted photos of himself with the dead animal on social media.
While those involved in the camera project are hopeful their AI devices can have an impact, they know they cannot be the sole solution.
In September, they are going to start trialling smells, sounds and lights at the camera sites to try to deter snow leopards from moving onto nearby villages, putting themselves and livestock in jeopardy.
Their work tracking these “ghosts of the mountains” is not over yet.
– Azadeh Moshiri, Usman Zahid and Kamil Khan Dayan
(BBC News)
FEATURES
Asweddumized fields and sizzling kottu roti: New words from Sri Lanka
Published
5 days agoon
June 26, 2025By
editor
In a letter dated 7 October 1971 and sent from Panadura, Ceylon, OED contributor Pearl Cooray wrote to then Chief Editor Robert Burchfield: ‘I have looked up references for the word asweddumize and have succeeded to a certain extent. The Sinhala word aswedduma means “land recently converted into a paddy field”, and the Anglicized word asweddumize means to prepare a field for sowing paddy’. Cooray was a Sri Lankan academic who visited Burchfield in Oxford earlier in 1971, and upon returning to her country and her position in the Dictionary Department of the University of Ceylon, briefly corresponded with the OED, sending the above quoted letter as well as a selection of Sri Lankan newspapers and magazines for the reading programme for the OED Supplements that were in preparation at the time. Her suggestion for asweddumize would have been too late for the word to be considered for Volume I of the Supplements, so Burchfield wrote the word and definition on a paper slip, the main means by which words were tracked until the 2010s, and filed it alongside an earlier slip from July 1970 with the same suggestion from another Sri Lankan contributor, D. N. Ponnamperuma.
Nothing further is found about asweddumize in the OED’s files until 1986, when botanist D. J. Mabberley, a regular consultant for the Supplement, sent in a quotation slip for the word, which he would have encountered during the time he spent at a university in Sri Lanka. A decade later, another slip records the decision made not to draft an entry for asweddumize due to lack of evidence. ‘Omit (sadly)’was the responsible editor’s regretful note on the slip.
Almost thirty years later, this sad omission has finally been rectified, with the addition of asweddumize to the OED as part of this update. Current OED Sri Lankan English consultant Rochana Jayasinghe’s research on Pearl Cooray and her contributions to the Supplement helped put asweddumize back on the OED’s radar, and now that the dictionary’s editors have wider access to historical and contemporary Sri Lankan sources than their counterparts in the 1970s and 80s, it was possible to find sufficient evidence for the word, including a first quotation from as far back as 1857.
Joining asweddumize among this batch of new words are other borrowings from Sinhala, the Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese, the largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka. Mallung (first attested 1893) is lightly cooked, shredded (often leafy green) vegetables mixed with fresh grated coconut, chilli, and other spices, served as a side dish, salad, or condiment as part of a typical Sri Lankan meal, while kiribath (1886) is a Sri Lankan dish made with rice cooked in coconut milk and formed into a block, typically sliced into diamond-shaped pieces and served with various types of onion relish or sweetened with jaggery. Kiribath is traditionally eaten at special occasions such as Avurudu (1881), the first day of the Sinhala and Hindu New Year, occurring on the spring equinox (usually falling around 14 April), marked by a period of celebration typically lasting for seven to ten days.
Other Sri Lankan English words in this update originate both in Sinhala and another widely spoken language on the island, Tamil. Kottu roti (1991) is a Sri Lankan dish consisting of pieces of roti, meat, and vegetables, mixed with spices and curry sauce, and chopped by cleavers as they are cooked on a griddle. It is typically associated with the distinctive sound of the cleavers hitting the griddle as it is prepared by roadside vendors, and its name combines the Tamil word kottu ‘chopped’ with the Sinhala word roṭi ‘bread’. Partly a borrowing from Sinhala and partly a borrowing from Tamil, watalappam (1956) is a custard made from coconut milk (or sometimes condensed milk), cashew nuts, eggs, and spices such as cardamom and cloves, sweetened with jaggery and traditionally eaten by Sri Lankan Muslims during celebrations marking the end of Ramadan.
Sri Lankan music is represented by the words baila (1973) and papare (2006). Baila, a loan word from Portuguese, refers to an uptempo style of popular music originating in Sri Lanka which combines influences from both Africa and Europe, typically played in 6-8 time, with a syncopated rhythm, as well as to the style of dance performed to this music. Often associated with weddings and other celebrations, types of baila music are also popular in Goa and in the city of Mangaluru, on India’s west coast. Papare, on the other hand, is a genre of Sri Lankan music usually played at cricket and other sports matches, characterized by lively rhythms and typically featuring instrumentation of trumpet, saxophone, trombone, and snare and bass drums.
Apart from adding new Sri Lankan English words, OED editors have also revised a number of existing Sri Lankan English entries in the dictionary. Both these new and revised entries have been given transcriptions and audio pronunciations based on a new pronunciation model for Sri Lankan English, which is explained in more detail in this article. These enhancements to the OED’s coverage of Sri Lankan English help provide a more complete picture of how the language is used islandwide.
Full list of World English additions and revisions in the OED June 2025 update
(oed.com)
FEATURES
Dog-sized dinosaur that ran around feet of giants discovered
Published
6 days agoon
June 25, 2025By
editor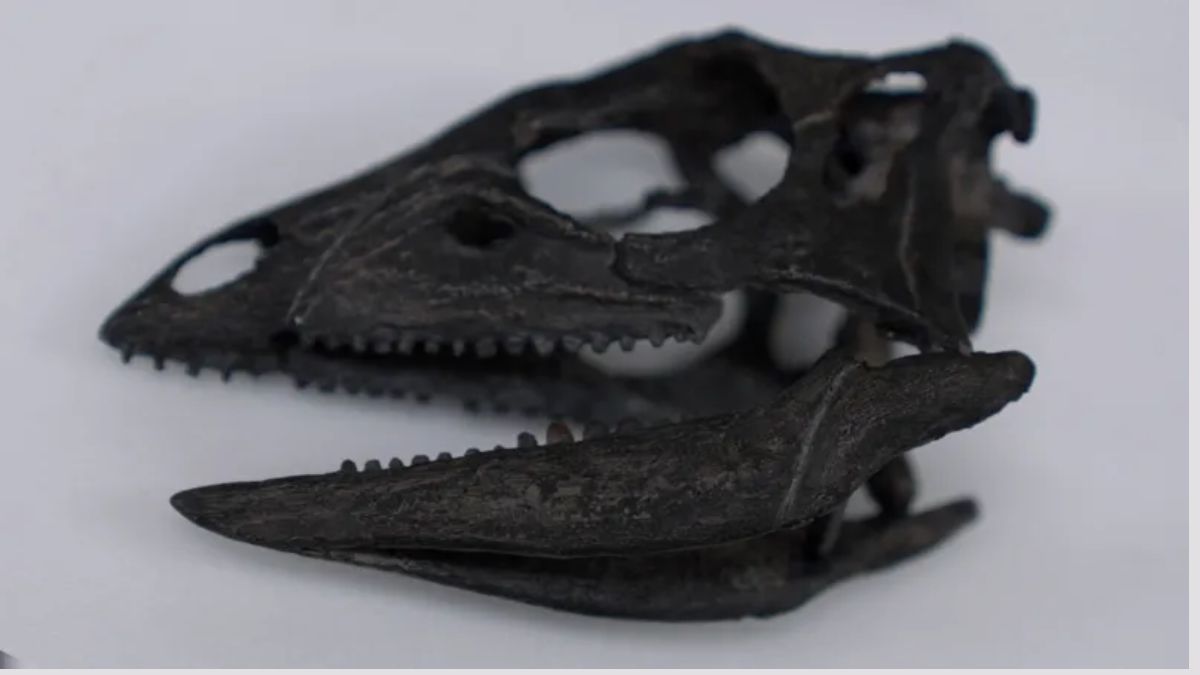
The full name of the new species is Enigmacursor mollyborthwickae dinosaur
A labrador-sized dinosaur was wrongly categorised when it was found and is actually a new species, scientists have discovered.
Its new name is Enigmacursor – meaning puzzling runner – and it lived about 150 million years ago, running around the feet of famous giants like the Stegosaurus.
It was originally classified as a Nanosaurus but scientists now conclude it is a different animal.
On Thursday it will become the first new dinosaur to go on display at the Natural History Museum (NHM) in London since 2014.
BBC News went behind the scenes to see the dinosaur before it will be revealed to the public.
The discovery promises to shed light on the evolutionary history that saw early small dinosaurs become very large and “bizarre” animals, according to Professor Paul Barrett, a palaeontologist at the museum.
When we visit, the designer of a special glass display case for the Enigmacursor is making last-minute checks.
The dinosaur’s new home is a balcony in the museum’s impressive Earth Hall. Below it is Steph the Stegosaurus who also lived in the Morrison Formation in the Western United States.
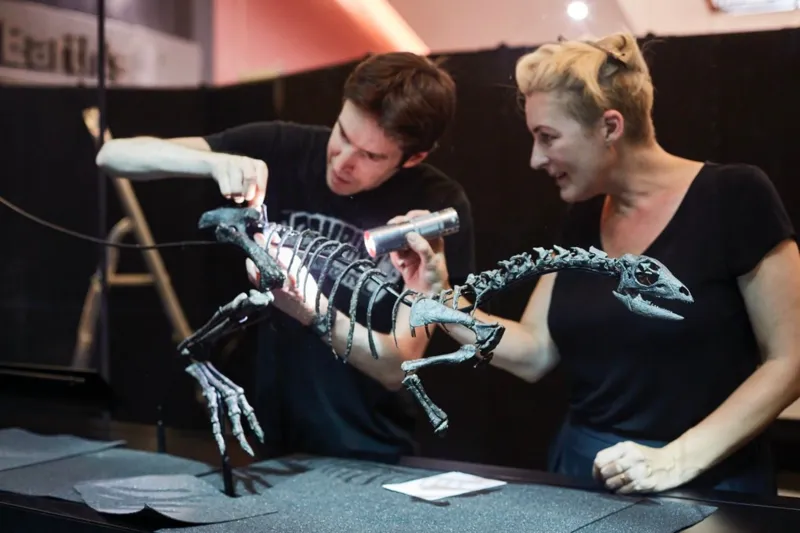
Enigmacursor is tiny by comparison. At 64 cm tall and 180 cm long it is about the height of a labrador, but with much bigger feet and a tail that was “probably longer than the rest of the dinosaur,” says Professor Susanna Maidment.
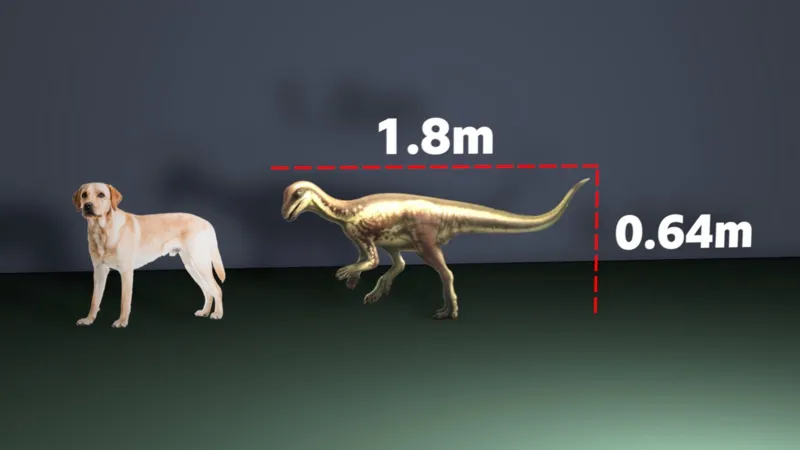
The Enigmacursor was a small dinosaur that lived alongside some of the biggest known
“It also had a relatively small head, so it was probably not the brightest,” she adds, adding that it was probably a teenager when it died.
With the fossilised remains of its bones in their hands, conservators Lu Allington-Jones and Kieran Miles expertly assemble the skeleton on to a metal frame.
“I don’t want to damage it at this stage before its revealed to everybody,” says Ms Allington-Jones, head of conservation.
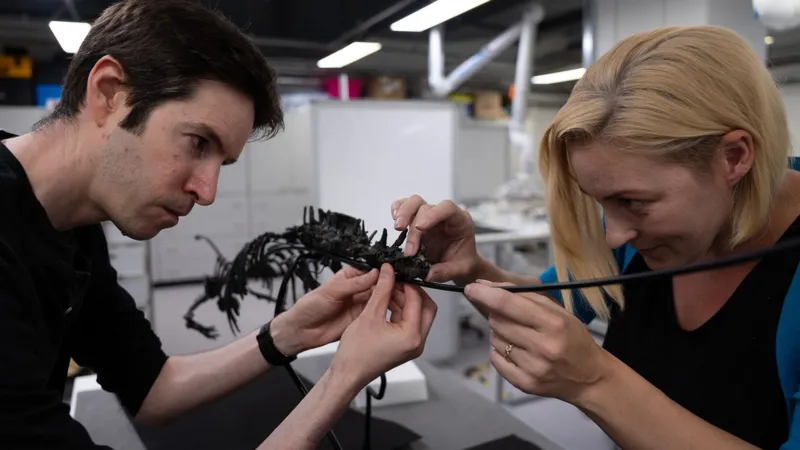

Conservators Lu Allington-Jones and Kieran Miles assembled the dinosaur onto a frame for display
“Here you can see the solid dense hips showing you it was a fast-running dinosaur. But the front arms are much smaller and off the ground – perhaps it used them to shovel plants in its mouth with hands,” says Mr Miles.
It was clues in the bones that led scientists at NHM to conclude the creature was a new species.
“When we’re trying to identify if something is a new species, we’re looking for small differences with all of the other closely-related dinosaurs. The leg bones are really important in this one,” says Prof Maidment, holding the right hind limb of the Enigmacursor.
When the dinosaur was donated to the museum it was named Nanosaurus, like many other small dinosaurs named since the 1870s.
But the scientists suspected that categorisation was false.
To find out more, they travelled to the United States with scans of the skeleton and detailed photographs to see the original Nanosaurus that is considered the archtype specimen.
“But it didn’t have any bones. It’s just a rock with some impressions of bone in it. It could be any number of dinosaurs,” Professor Maidment said.
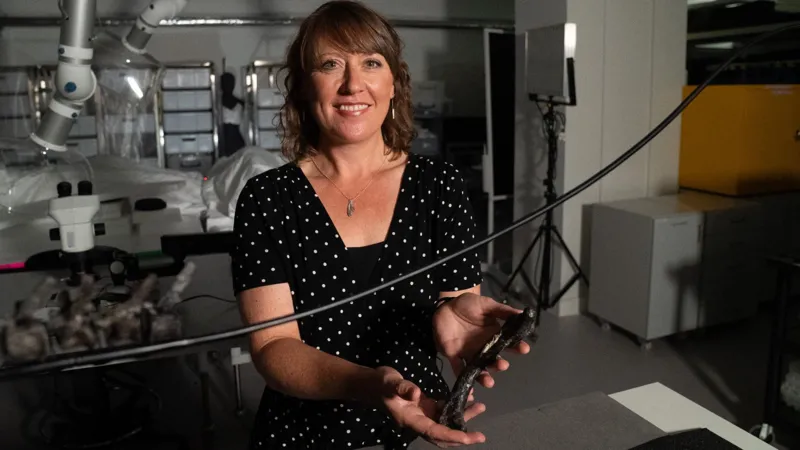

Susanna Maidment travelled to the US to look at the original Nanosaurus dinosaur
In contrast, the NHM’s specimen was a sophisticated and near-to-complete skeleton with unique features including its leg bones.
Untangling this mystery around the names and categorisation is essential, the palaeontologists say.
“It’s absolutely foundational to our work to understand how many species we actually have. If we’ve got that wrong, everything else falls apart,” says Prof Maidment.
The scientists have now formally erased the whole category of Nanosaurus.
They believe that other small dinosaur specimens from this period are probably also distinct species.
The discovery should help the scientists understand the diversity of dinosaurs in the Late Jurassic period.
Smaller dinosaurs are “very close to the origins of the large groups of dinosaurs that become much more prominent later on,” says Prof Barrett.
“Specimens like this help fill in some of those gaps in our knowledge, showing us how those changes occur gradually over time,” he adds.
Looking at these early creatures helps them identify “the pressures that finally led to the evolution of their more bizarre, gigantic descendants,” says Prof Barrett.

The fossilised remains are the most complete of any in the world for early small dinosaurs
The scientists are excited to have such a rare complete skeleton of a small dinosaur.
Traditionally, big dinosaur bones have been the biggest prize, so there has been less interest in digging out smaller fossils.
“When you’re looking for those very big dinosaurs, sometimes it’s easy to overlook the smaller ones living alongside them. But now I hope people will keep their eyes close to the ground looking for these little ones,” says Prof Barrett.
The findings about Enigmacursor mollyborthwickae are published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
– Georgina Rannard
Science correspondent
(BBC News)
FEATURES
JVP-NPP should learn difference between “marine research” & “surveillance”
Published
1 week agoon
June 21, 2025By
editor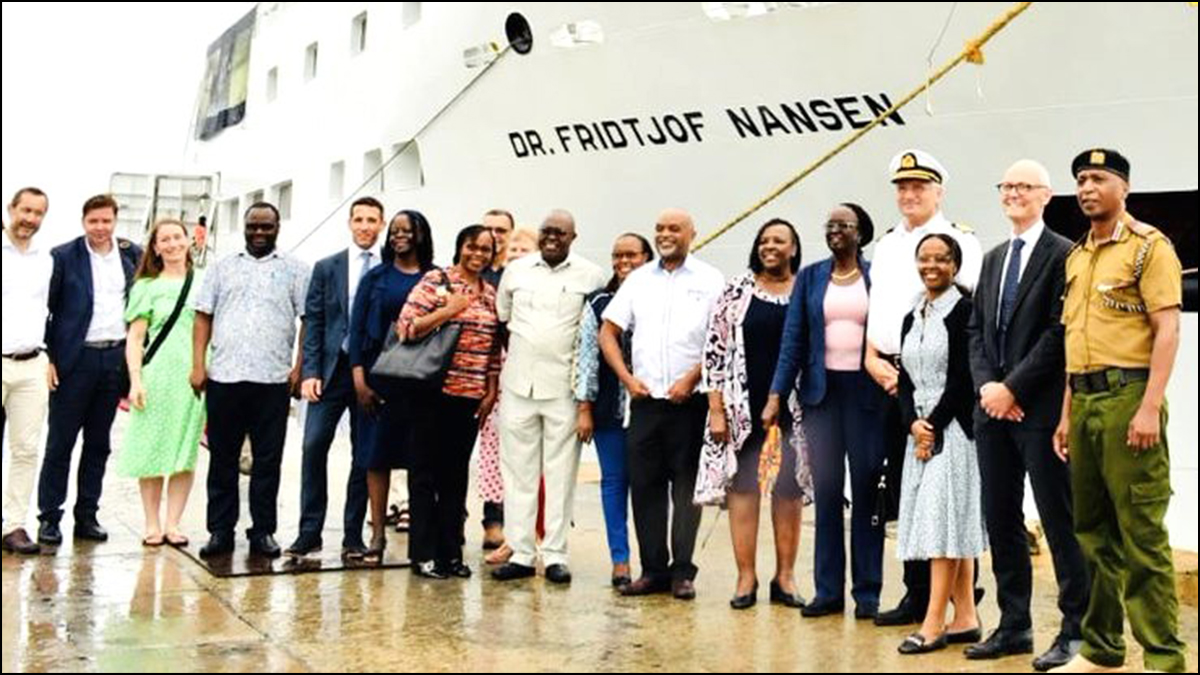

There’s now an apparent stand-off between the UN FAO and the Foreign Affairs Minister Vijitha Herath on the request made by the FAO to have permission for the UN flagged “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel to enter Sri Lankan waters. Minister Herath is on record saying the request would have to wait till the Committee on Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for foreign research vessels appointed by him and perhaps chaired by him too, complete their task in formulating the SOP. It was revealed, the SOP Committee is yet to be convened for the first time. With “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel waiting in Mauritius to set sail to Sri Lanka, numerous discussions the UN had with the Foreign Ministry (FM) since April has only reached the point, where the SL FM agreed to allow the ship to pick Bangladeshi “Scientists” from Colombo, but not get involved in any research in our waters.
res (SOP) for foreign research vessels appointed by him and perhaps chaired by him too, complete their task in formulating the SOP. It was revealed, the SOP Committee is yet to be convened for the first time. With “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel waiting in Mauritius to set sail to Sri Lanka, numerous discussions the UN had with the Foreign Ministry (FM) since April has only reached the point, where the SL FM agreed to allow the ship to pick Bangladeshi “Scientists” from Colombo, but not get involved in any research in our waters.
What’s this whole calamity over a FAO marine research ship requesting permission to enter Sri Lankan waters? Someone somewhere at the helm of the Foreign Ministry, or the Foreign Minister himself has wholly misinterpreted the issue of country owned research ships visiting Sri Lanka and the moratorium that was imposed by President Wickramasinghe barring foreign research ships.
Sri Lanka was pressured by India and the US to curtail if not stop Chinese research ships from docking in our ports in the past few years. Special concerns were over the 02 research ships “Yuan Wang 5” that docked at Hambantota in early 2022 during Gotabhaya’s presidency and “Shi Yan 6” in October 2023 at the Colombo port during Wickramasinghe’s presidency. It was said, these 02 research ships had the capacity for surveillance and monitoring the region. Under pressure especially from New Delhi, President Wickramasinghe decided to impose a one year moratorium on foreign research ships visiting Sri Lanka, effective from early January 2024.

The Wickramasinghe moratorium came to its end on 05 January 2025, as the JVP-NPP government did not extend it further. Reason to allow the moratorium to lapse in January, may have been on a strictly confidential agreement reached to have a separate bi-lateral agreement on defence, during President Anura Kumara’s maiden official visit to India in mid-December 2024. Defence had been an issue discussed with Indian authorities during President Anura Kumara’s Indian visit, wrote Dr. Samatha Mallempati of “Indian Council of World Affairs” in May 2025. A defence MoU would thus make the moratorium irrelevant thereafter. PM Modi was to visit Sri Lanka 04 months later in early April this year. One among the many MoUs the 02 governments signed during PM Modi’s visit was the first ever Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on “defence co-operation”.
India began working on a defence strategy for Indian Ocean Region (IOR) since the conclusion of Sri Lanka’s North-East civil war in 2009. New Delhi was very much concerned over President Rajapaksa’s post-war association with not only China, but with Pakistan too. Both with long time hostile border disputes with India. Contributing an article to “Stimson.org” on Pakistan-Sri Lanka relations in March 2021, two researchers on South & East Asian geo-politics Riaz Khokhar and Asma Khalid wrote, “In 2016, Pakistan signed a defense agreement with Sri Lanka to provide Colombo with eight JF-17 fighter aircrafts. Pakistani and Sri Lankan armies and naval forces have also regularly interacted through port calls, military and naval training and exercises, and defense workshops and seminars. In the recent high-level visit to Colombo, the Pakistani premier offered a USD $50 million credit line to Sri Lanka to further enhance defense and security partnerships.”
South Asian geo-politics did have new developments with post-war Sri Lanka compromising its economic needs with defence and national security in challenging the Tamil Diaspora canvassed US-Euro resolutions at UNHRC Sessions. Rajapaksa government was required to accept independent international investigations on war crimes and crimes against humanity, with many top military officers named. Pakistan stood with Sri Lanka, voting against all such resolutions at every UNHRC Session, while the Rajapaksa regime joined the Belt and Road Initiative of China, and was financially supported by China. Financial support that led to the popular adage “Sri Lankan type Chinese debt trap”.
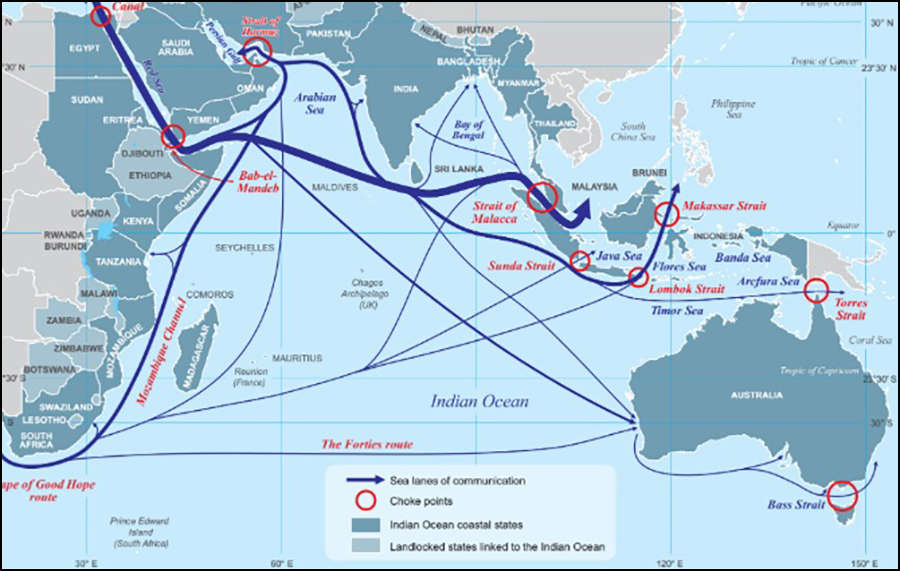
India has since been working towards establishing its dominance in the IOR keeping Sri Lanka as its focal point. Highlighting the geo-political importance of Sri Lanka, Dr. Samatha Mallempati wrote, “Since the region accounts for fifty percent of world maritime trade and seventy percent of global trade in oil and gas, there is a greater need to safeguard the sea lanes of communication. The increasing strategic significance of island states in the region therefore assumed importance. The island states such as Sri Lanka is looking to play a much bigger role by leveraging their geographical location.”
The perception in New Delhi that Sri Lanka is leveraging its geographical location to define geo-politics in the IOR, was what paved for the MoU on defence co-operation India signed with Sri Lanka, that for 05 years would provide India adequate space to influence Sri Lankan geo-politics in its favour. But the fact is, all these agreements and treaties are about IOR peace and stability and the influence “foreign countries” may have in it. The Sri Lankan moratorium was also about research ships of foreign countries, docking in our ports.
How would the UN flagged marine research ship “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” interfere in IOR stability and peace? The request to FAO for marine research in our waters had gone from the SL Government, never mind who led the government. FAO is focussed on sustainable fisheries management and this modern, fully equipped ship for marine research is used mainly in African and Indian Ocean waters in collaboration with NORAD to support developing countries with research based fisheries management. That perhaps was the only reason for the previous government to request the FAO to visit Sri Lankan waters. Mind you, that request for FAO to undertake marine research in our waters, went out while the moratorium on foreign research ships was fully effective.
Whatever the bureaucracy at the FM says, a seasoned politician like Vijitha Herath who had been in parliament for 25 years to date from year 2000, should know the difference between this UN flagged marine research ship and other research ships owned by individual countries. Anything flagged as “UN” is common property of 195 sovereign nation States who are UN members. This ignorance therefore very clearly exhibits the JVP/NPP leadership as the most intellectually timid leadership to have been voted to power since 1948 independence.
Kusal Perera
20 June, 2025

A few showers expected today

Fuel prices upped
























