FEATURES
In appreciation of Professor Kumar David
Published
9 months agoon
By
editor
Professor Kumar David, once an academic in the Engineering Faculty, Peradeniya University, and a Fellow of the Institution of Electrical Engineers in the UK and Hong Kong has left for eternal rest, last Monday while in Los Angeles, USA. We believe the “left” leaning English reader would miss Kumar’s forays into political controversies, with his own reading of issues that often provided dissenting, but populist perspectives, he developed over the decades since leaving the NSSP in 1980 July. Politically, he was advocating for “unity in the scattered left”.
Professionally too, he stood out as an exceptional, pragmatic thinker and was accepted for that. We believe he still remains the youngest to be appointed to the Director Board of the CEB way back in 1970, perhaps after the change of government in July. Kumar would not have been 30 years then. He was also a strong critic of the Mahaweli Development power generation scheme in 1979, when the blueprint was out for academic observation.
For us, Kumar was an interesting polemicist in our initial group of young Samasamaja activists, when we were into “entryism” trying to turn around the LSSP to its pre-coalition, Trotskyite politics of 1964. From among other academics including Wickramabahu, Sumanasiri, Shantha de Alwis, Nalin de Silva, Chris Rodrigo, who were key players in this small activist group labelled “Waama-Samasamajaya”, Kumar stood out as a frank and a blunt intervener in any discussion, when he had to disagree. He was a unique character in many ways. He was hard-hitting, sarcastic and witty in debates, at times consciously mispronouncing Sinhala terms or using them at the wrong place, gaining all the attention he wanted in discussions.
Kumar’s strength was his ability to politically see through issues. We remember his reading of the outcome on the 1980 July strike. A fortnight before the July strike he resigned from the NSSP Central Committee wanting to take up an academic post in Zimbabwe. We met him crossing the Jawatte Road, opposite his residence in the early afternoon, on the day he was to leave Sri Lanka for Zimbabwe. He asked us how the strike was turning out. Ridiculing our optimism he said, “Macho, JR would simply crush the whole strike mercilessly, in a few days. What general strike with some clerks? This era you need to have the CEB and Rupavahini out on strike, if you want Jayawardene to listen to your demands”. He was no doubt right.
At barricades too when protesting on political issues, he would guess the response of the police, just looking at them. He often stood right in front with his broad frame, far taller than all others, with an untanned brown beard, creating an elite, dominant personality in him that police officers too respected when engaging with him. He was from a very elite background no doubt, with high profile Jaffna Catholic family roots. His father was a district judge and few others in the immediate family circle too were judges and lawyers.
A frequent visitor to Sri Lanka on a Sri Lankan passport, for he was no dual citizen, Kumar was quite familiar with local political issues and wrote his own interpretation on them in mainstream media. His high-flown English was very readable with his knack for wit and sarcasm and most would not miss his name in print media. So were we, despite our political differences and perspectives.
He was a dominating personality in any forum and his interventions would be missed by most in “left of centre” Sri Lankan politics. We share our grief with Rohini and his family, and with that of all others in Sri Lankan “left” and democratic politics. Thank you Kumar for all your contributions and companionship, we cherish with camaraderie.
– Siritunge Jayasuriya (General Secretary – USP)
– Kusal Perera (Political Essayist)
You may like
-


President meets Gates Foundation delegation
-


TUs oppose appointment of Premarathne as new Excise chief
-


CCC calls for ‘continued engagement’ on US tariff reduction
-


US trade tariffs : GoSL to continue talks
-


China to drift away from SL with Mazagon Dock’s purchase of CDPLC?
-


Daycare centres for children with Autism & Neurodevelopmental disorders
FEATURES
Will JVP/NPP leaders respond to this, while dabbling on populist politics?
Published
4 days agoon
July 7, 2025By
editor
Half this year 2025 has also been spent with no answer to how Sri Lanka would begin settling its restructured foreign debts and interests on them, from year 2028 August. When President Wickramasinghe led government began discussing its foreign debt restructuring with the IMF framed within IMF conditions, Sri Lanka had amassed a massive USD 56,092.95 million by end third quarter 2024, the time we were tied to presidential election campaigns.
The last quarter with parliament elections also slotted in, the new President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD), sworn in late September last year, had no time to intervene in the economy. Thus the fourth quarter of the year 2024, the first 03 months of President AKD’s rule closed in December with foreign debt increasing to USD 57,133.49 million. An increase of USD 1,040.54 million in 03 months. Sri Lanka had by then agreed with IMF to restructure USD 12.55 billion of its total debts.
According to the IMF agreement signed by President AKD’s NPP government, Sri Lanka has to begin repayments from 2028 August. That would be under AKD’s NPP rule.
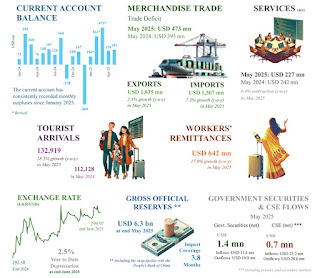
Meanwhile Sri Lanka has to settle this year 2025, a total of USD 2,454 million in routine debts including USD 1,085 million as interest, according to Deputy Minister of Economic Development, Anil Jayantha. That, excluding the annual foreign trade deficit the GoSL has to settle every year.
In year ending December 2024, the total foreign trade deficit was USD 6,100 million with an import bill of USD 18,841 million, an increase of 12.1 percent over the previous year, despite fuel imports decreasing. This year 2025, the trade deficit in month of May was USD 473 million, according to the CBSL figures published. This was an increase of 16.9 percent over previous year trade deficit in month of May.
We are in the midst of a two year Middle East armed conflict, that may drag on, even if it does not lead to a cease fire between Israel, Iran and the Hamas armed organisation in Palestine. Uncertainties looming in Middle East may not provide the dollar remittances from migrant labour the government estimated for this whole year and received during the past 05 months. Thus, GoSL may have to face a serious increase in the external trade deficit, if a miracle does not make a change. Assumed the increase would be around 10 percent over the previous year 2024, the external trade deficit may reach or even go beyond USD 6,710 million. To this, has to be added the annual routine debt of USD 2,454 million disclosed by Deputy Minister Jayantha in parliament, to have the total commitment of the GoSL for year 2025. That then would be USD 9,164 million in 2025.
As much as the NPP government, the SJB in Opposition is inefficient and intellectually timid too in responding to governance issues. Thus there is no serious, intellectual debate in how the government could earn the extra USD 9,164 million needed to bridge the trade deficit this 2025. The IMF has no proposal for increased exports to fetch extra dollars. They are only focussed on axing State expenses and increasing “Rupee income” with increased taxing. The IMF thus approved import of luxury vehicles as a source of Rupee income from taxes, wholly ignoring the fact, GoSL would have to burn a heavy load of hard earned dollars including remittances from migrant labour. From January this year till beginning of month of May, Sri Lanka had spent USD 200 million for vehicle imports, according to CBSL Governor Dr. Nandalal Weerasinghe. He told media on 22 May, the total value of Letters of Credit opened by then for vehicle imports was USD 450 million. And the NPP government seems happy with a tax collection of Rs.136 billion by end of April.
Now, what is important? Collecting 136 billion rupees, form spending USD 200 million for vehicles, that would need extra dollars for extra consumption of fuel, with greater traffic congestions on urban roads? Fact remains, the IMF has no programme, no proposal to increase the export and service income despite all tax concessions, privileges and State patronage for FDIs and for tourism development given by the State at the expense of the tax payer. The annual gap between import trade cost and the export trade income remains around USD 7,000 to 8,000 million with another USD 2,000 million required for debt servicing.
This should be stressed without ambiguity. The required extra annual income in many millions of dollars cannot be earned with Ministers reducing numbers in their vehicle fleet, from not taking residency in official bungalows, from reducing State expenses in patches, from Ministers stepping into paddy fields carrying a mammoty, or by indicting few officials and politicians of the previous regime.
We need a well designed national development plan that can guarantee annual increase in dollar exports to bridge a trade deficit of about USD 10,000 million. Will the JVP/NPP leadership tell the People what their plan is for such income earning, while going round with their populist propaganda stuff?
– Kusal Perera
FEATURES
Asweddumized fields and sizzling kottu roti: New words from Sri Lanka
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 26, 2025By
editor
In a letter dated 7 October 1971 and sent from Panadura, Ceylon, OED contributor Pearl Cooray wrote to then Chief Editor Robert Burchfield: ‘I have looked up references for the word asweddumize and have succeeded to a certain extent. The Sinhala word aswedduma means “land recently converted into a paddy field”, and the Anglicized word asweddumize means to prepare a field for sowing paddy’. Cooray was a Sri Lankan academic who visited Burchfield in Oxford earlier in 1971, and upon returning to her country and her position in the Dictionary Department of the University of Ceylon, briefly corresponded with the OED, sending the above quoted letter as well as a selection of Sri Lankan newspapers and magazines for the reading programme for the OED Supplements that were in preparation at the time. Her suggestion for asweddumize would have been too late for the word to be considered for Volume I of the Supplements, so Burchfield wrote the word and definition on a paper slip, the main means by which words were tracked until the 2010s, and filed it alongside an earlier slip from July 1970 with the same suggestion from another Sri Lankan contributor, D. N. Ponnamperuma.
Nothing further is found about asweddumize in the OED’s files until 1986, when botanist D. J. Mabberley, a regular consultant for the Supplement, sent in a quotation slip for the word, which he would have encountered during the time he spent at a university in Sri Lanka. A decade later, another slip records the decision made not to draft an entry for asweddumize due to lack of evidence. ‘Omit (sadly)’was the responsible editor’s regretful note on the slip.
Almost thirty years later, this sad omission has finally been rectified, with the addition of asweddumize to the OED as part of this update. Current OED Sri Lankan English consultant Rochana Jayasinghe’s research on Pearl Cooray and her contributions to the Supplement helped put asweddumize back on the OED’s radar, and now that the dictionary’s editors have wider access to historical and contemporary Sri Lankan sources than their counterparts in the 1970s and 80s, it was possible to find sufficient evidence for the word, including a first quotation from as far back as 1857.
Joining asweddumize among this batch of new words are other borrowings from Sinhala, the Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese, the largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka. Mallung (first attested 1893) is lightly cooked, shredded (often leafy green) vegetables mixed with fresh grated coconut, chilli, and other spices, served as a side dish, salad, or condiment as part of a typical Sri Lankan meal, while kiribath (1886) is a Sri Lankan dish made with rice cooked in coconut milk and formed into a block, typically sliced into diamond-shaped pieces and served with various types of onion relish or sweetened with jaggery. Kiribath is traditionally eaten at special occasions such as Avurudu (1881), the first day of the Sinhala and Hindu New Year, occurring on the spring equinox (usually falling around 14 April), marked by a period of celebration typically lasting for seven to ten days.
Other Sri Lankan English words in this update originate both in Sinhala and another widely spoken language on the island, Tamil. Kottu roti (1991) is a Sri Lankan dish consisting of pieces of roti, meat, and vegetables, mixed with spices and curry sauce, and chopped by cleavers as they are cooked on a griddle. It is typically associated with the distinctive sound of the cleavers hitting the griddle as it is prepared by roadside vendors, and its name combines the Tamil word kottu ‘chopped’ with the Sinhala word roṭi ‘bread’. Partly a borrowing from Sinhala and partly a borrowing from Tamil, watalappam (1956) is a custard made from coconut milk (or sometimes condensed milk), cashew nuts, eggs, and spices such as cardamom and cloves, sweetened with jaggery and traditionally eaten by Sri Lankan Muslims during celebrations marking the end of Ramadan.
Sri Lankan music is represented by the words baila (1973) and papare (2006). Baila, a loan word from Portuguese, refers to an uptempo style of popular music originating in Sri Lanka which combines influences from both Africa and Europe, typically played in 6-8 time, with a syncopated rhythm, as well as to the style of dance performed to this music. Often associated with weddings and other celebrations, types of baila music are also popular in Goa and in the city of Mangaluru, on India’s west coast. Papare, on the other hand, is a genre of Sri Lankan music usually played at cricket and other sports matches, characterized by lively rhythms and typically featuring instrumentation of trumpet, saxophone, trombone, and snare and bass drums.
Apart from adding new Sri Lankan English words, OED editors have also revised a number of existing Sri Lankan English entries in the dictionary. Both these new and revised entries have been given transcriptions and audio pronunciations based on a new pronunciation model for Sri Lankan English, which is explained in more detail in this article. These enhancements to the OED’s coverage of Sri Lankan English help provide a more complete picture of how the language is used islandwide.
Full list of World English additions and revisions in the OED June 2025 update
(oed.com)
FEATURES
Dog-sized dinosaur that ran around feet of giants discovered
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 25, 2025By
editor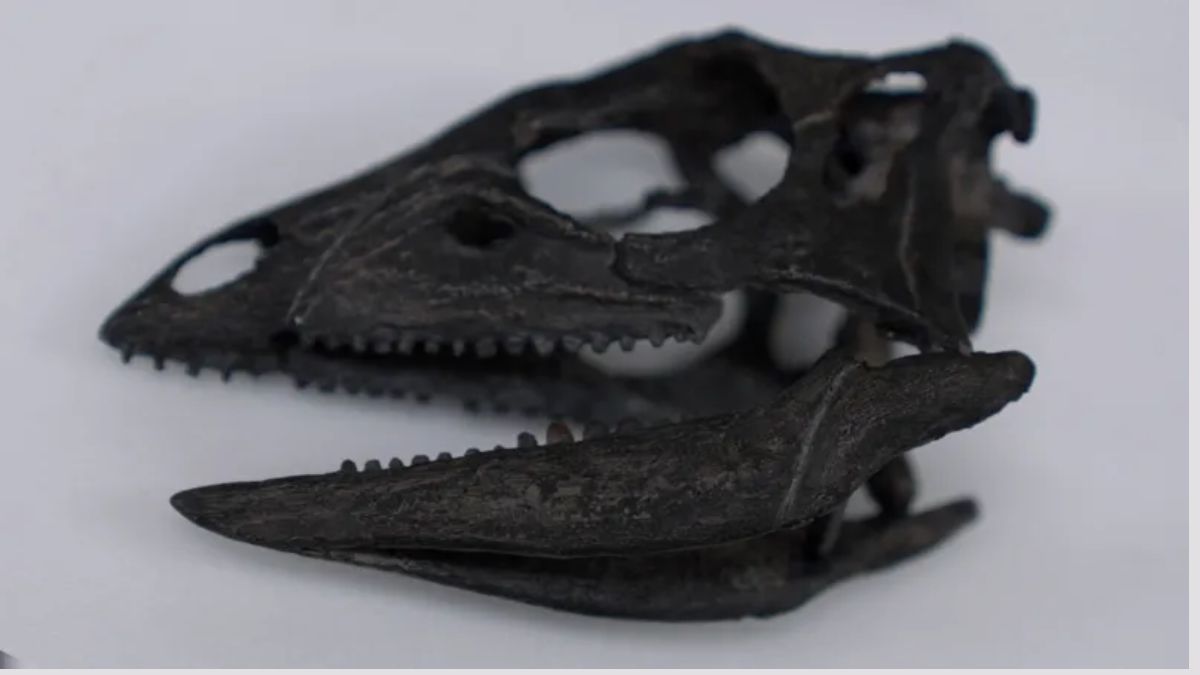
The full name of the new species is Enigmacursor mollyborthwickae dinosaur
A labrador-sized dinosaur was wrongly categorised when it was found and is actually a new species, scientists have discovered.
Its new name is Enigmacursor – meaning puzzling runner – and it lived about 150 million years ago, running around the feet of famous giants like the Stegosaurus.
It was originally classified as a Nanosaurus but scientists now conclude it is a different animal.
On Thursday it will become the first new dinosaur to go on display at the Natural History Museum (NHM) in London since 2014.
BBC News went behind the scenes to see the dinosaur before it will be revealed to the public.
The discovery promises to shed light on the evolutionary history that saw early small dinosaurs become very large and “bizarre” animals, according to Professor Paul Barrett, a palaeontologist at the museum.
When we visit, the designer of a special glass display case for the Enigmacursor is making last-minute checks.
The dinosaur’s new home is a balcony in the museum’s impressive Earth Hall. Below it is Steph the Stegosaurus who also lived in the Morrison Formation in the Western United States.
Enigmacursor is tiny by comparison. At 64 cm tall and 180 cm long it is about the height of a labrador, but with much bigger feet and a tail that was “probably longer than the rest of the dinosaur,” says Professor Susanna Maidment.
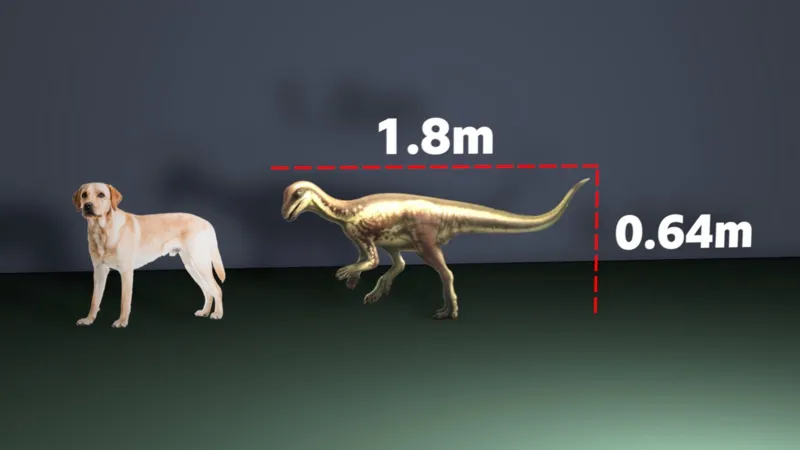
The Enigmacursor was a small dinosaur that lived alongside some of the biggest known
“It also had a relatively small head, so it was probably not the brightest,” she adds, adding that it was probably a teenager when it died.
With the fossilised remains of its bones in their hands, conservators Lu Allington-Jones and Kieran Miles expertly assemble the skeleton on to a metal frame.
“I don’t want to damage it at this stage before its revealed to everybody,” says Ms Allington-Jones, head of conservation.
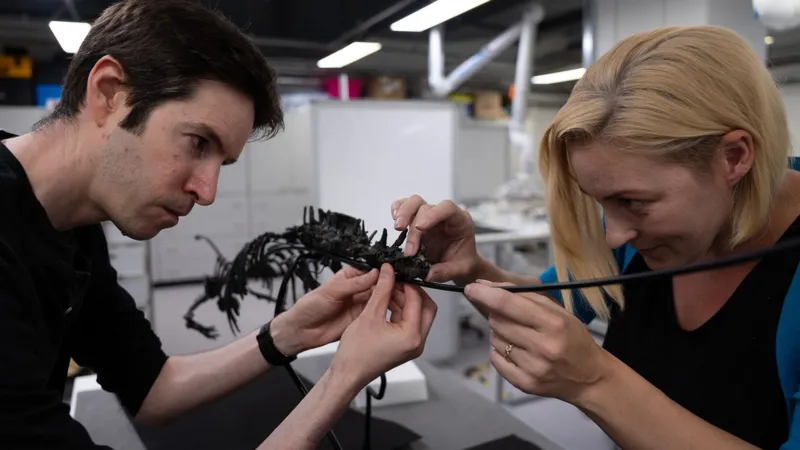

Conservators Lu Allington-Jones and Kieran Miles assembled the dinosaur onto a frame for display
“Here you can see the solid dense hips showing you it was a fast-running dinosaur. But the front arms are much smaller and off the ground – perhaps it used them to shovel plants in its mouth with hands,” says Mr Miles.
It was clues in the bones that led scientists at NHM to conclude the creature was a new species.
“When we’re trying to identify if something is a new species, we’re looking for small differences with all of the other closely-related dinosaurs. The leg bones are really important in this one,” says Prof Maidment, holding the right hind limb of the Enigmacursor.
When the dinosaur was donated to the museum it was named Nanosaurus, like many other small dinosaurs named since the 1870s.
But the scientists suspected that categorisation was false.
To find out more, they travelled to the United States with scans of the skeleton and detailed photographs to see the original Nanosaurus that is considered the archtype specimen.
“But it didn’t have any bones. It’s just a rock with some impressions of bone in it. It could be any number of dinosaurs,” Professor Maidment said.
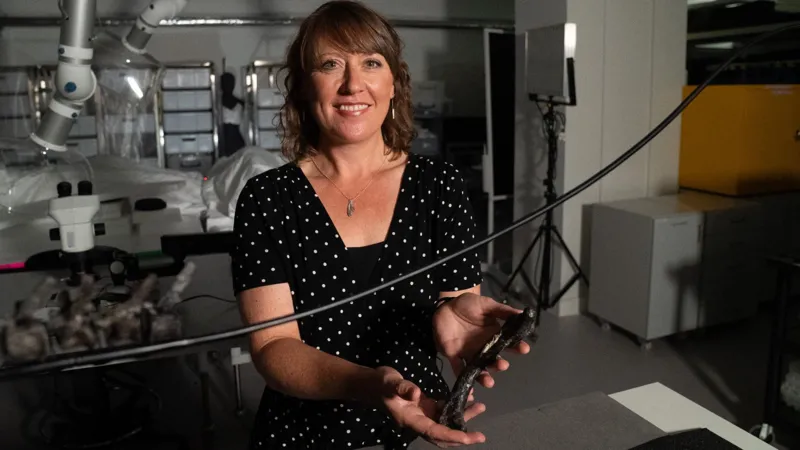

Susanna Maidment travelled to the US to look at the original Nanosaurus dinosaur
In contrast, the NHM’s specimen was a sophisticated and near-to-complete skeleton with unique features including its leg bones.
Untangling this mystery around the names and categorisation is essential, the palaeontologists say.
“It’s absolutely foundational to our work to understand how many species we actually have. If we’ve got that wrong, everything else falls apart,” says Prof Maidment.
The scientists have now formally erased the whole category of Nanosaurus.
They believe that other small dinosaur specimens from this period are probably also distinct species.
The discovery should help the scientists understand the diversity of dinosaurs in the Late Jurassic period.
Smaller dinosaurs are “very close to the origins of the large groups of dinosaurs that become much more prominent later on,” says Prof Barrett.
“Specimens like this help fill in some of those gaps in our knowledge, showing us how those changes occur gradually over time,” he adds.
Looking at these early creatures helps them identify “the pressures that finally led to the evolution of their more bizarre, gigantic descendants,” says Prof Barrett.
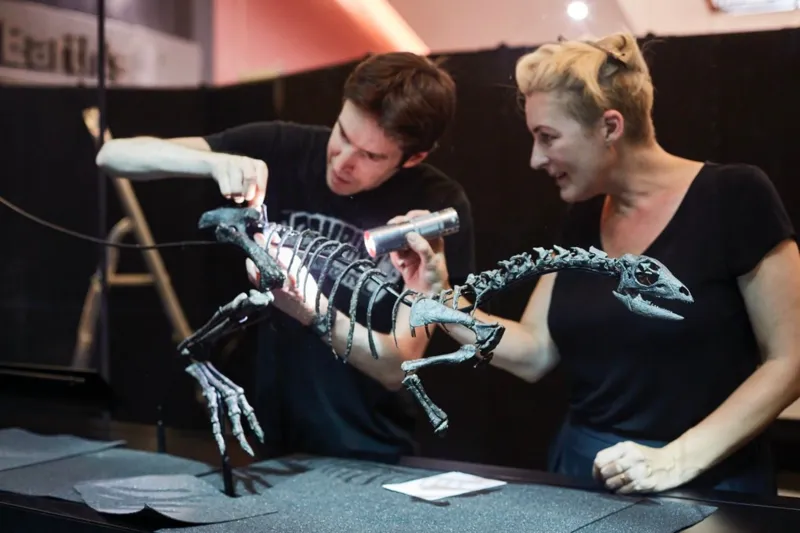

The fossilised remains are the most complete of any in the world for early small dinosaurs
The scientists are excited to have such a rare complete skeleton of a small dinosaur.
Traditionally, big dinosaur bones have been the biggest prize, so there has been less interest in digging out smaller fossils.
“When you’re looking for those very big dinosaurs, sometimes it’s easy to overlook the smaller ones living alongside them. But now I hope people will keep their eyes close to the ground looking for these little ones,” says Prof Barrett.
The findings about Enigmacursor mollyborthwickae are published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
– Georgina Rannard
Science correspondent
(BBC News)

President meets Gates Foundation delegation

TUs oppose appointment of Premarathne as new Excise chief














