FEATURES
The European towns that give away free chickens
Published
3 months agoon
By
editor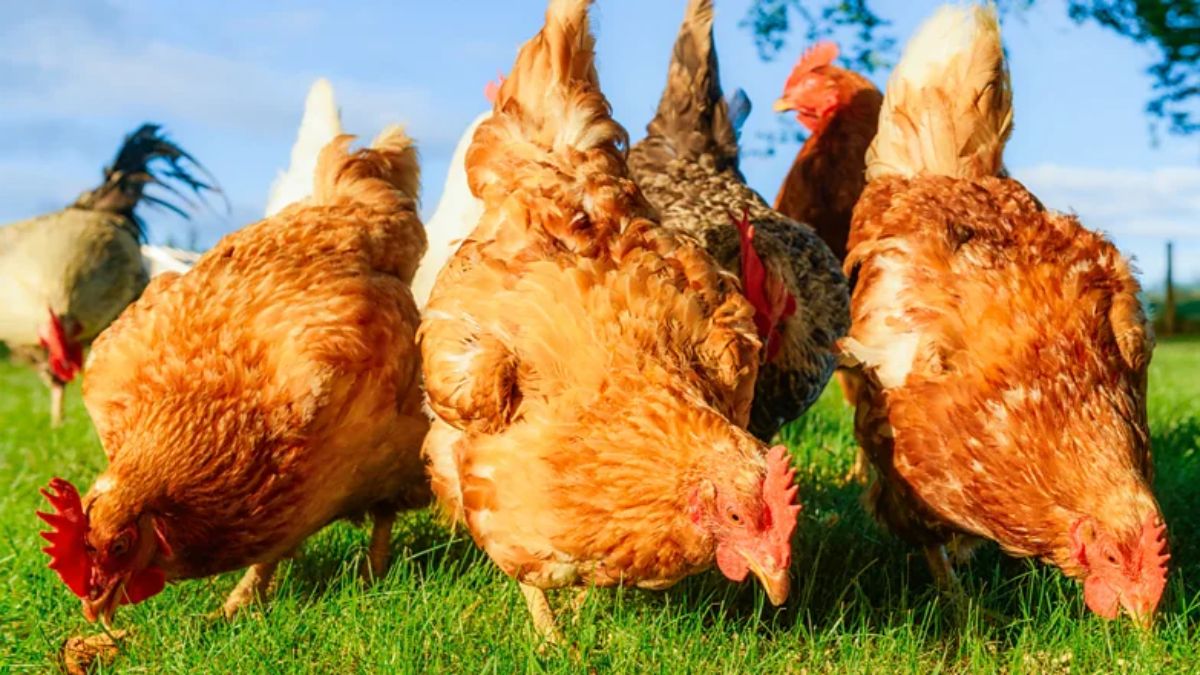
(Credit: Getty Images)
Towns in France and Belgium have been giving out free chickens for years to combat food waste – could the idea catch on elsewhere?
Around Easter in 2015, the small French village of Colmar started handing out free chickens to its residents. The aim of this experimental new scheme, launched by the waste collection department in the small village in north eastern France, was to reduce food waste.
The project had been in the works for some time. The then-president of Colmar Agglomération (a role similar to a mayor), Gilbert Meyer, had been reelected in 2014 with the slogan “one family, one hen”, which aimed to encourage residents to adopt a chicken. The following year the operation was launched, in partnership with two nearby chicken farms. Residents were encouraged to think of the free eggs – the effort put into raising a chicken would pay off quickly.
More than 200 homes in four municipalities signed up and were given two chickens each – either red chickens (Poulet Rouge) or Alsace chickens, an old and local breed.
Each household signed a pledge committing to raising the chickens, with the understanding that the waste department could conduct welfare spot checks on the animals at any time. Henhouses were not provided; it was up to the residents to build or buy their own. The department ensured that each home had enough space for the hens – between 8 and 10 sq m (86 and 108 sq ft).
The scheme was a success – and is still underway. “Over the years, other municipalities have joined and since 2022 all 20 municipalities of the agglomération have participated,” says Eric Straumann, current president of the Colmar Agglomération.
To date, 5,282 hens have been distributed to local residents, and applications are currently open for the next round of distribution in June 2025. Not only have the residents received a plentiful supply of free eggs, but food waste has also been averted from landfill as chickens are fed kitchen scraps which would otherwise be thrown away.
“Considering that a hen has a life expectancy of four years on average and that she consumes 150g (5.3oz) of bio-waste per day, we estimate that we have avoided 273.35 tonnes of bio-waste [since 2015],” says Straumann.

The small French village of Colmar has been handing out free chickens to its residents since 2015 (Credit: Getty Images)
Food waste contributes more methane emissions to the atmosphere than any other landfilled materials, due to its quick decay rate. In the US, around 58% of methane emissions released into the atmosphere from waste landfills are from food waste. Although shorter-lived in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide (CO2), methane has a global warming impact more than 80 times higher than CO2 over a 20-year period.
Around one third of food produced for humans is lost or wasted globally, amounting to 1.3 billion tonnes per year. Food loss and waste account for 8-10% of annual global greenhouse gas emissions – which is nearly five times the total emissions from the aviation sector.
Even though chicken owners in the UK have been advised to avoid to feeding the birds kitchen scraps due to concerns about spreading disease, it’s perfectly legal to do so elsewhere in the world, and it can have a meaningful impact on reducing food waste – and kickstart a cycle that benefits everyone.
“Proposed with the aim of reducing food waste, chickens make it possible to promote traditional circular economy practices that are still relevant today, particularly in villages, and which are now developing even in urban areas: chickens fed on our food waste in return provide us with fresh eggs,” says Straumann.
An additional benefit is that the chickens can teach children in Colmar about animals and the importance of protecting the natural world, he adds.
Colmar is not the only town to hand out free birds – nor was it the first to do so. In 2012 in another a small north-western French town called Pincé, two chickens were offered to each household to help them cut down on organic waste. “To begin with it was a joke, but then we realised it was a very good idea,” Lydie Pasteau, the mayor of Pincé, told local media at the time. A total of 31 families were given chickens, along with a bag of feed, with Pasteau calling the scheme a “surprising” success.
In Belgium, chickens have been handed out in the cities of Mouscron and Antwerp and the province of Limburg, although residents had to sign an agreement not to eat the chickens for at least two years. More than 2,500 families adopted hens in one year alone in Limburg, according to some reports, while in Mouscron, 50 pairs of chickens were given out in the second round of the scheme, after the initial giveaway was a success. Residents, who had to prove they had sufficient space in their gardens to keep the birds, were given basic instructions on chicken keeping.
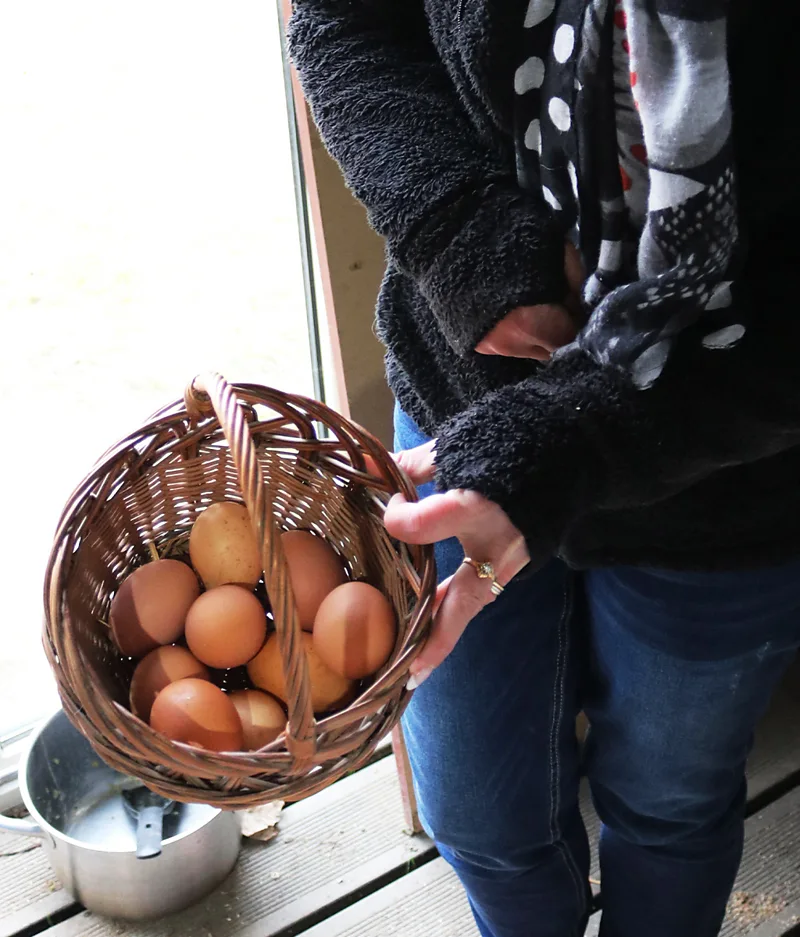

Colmar residents have been left with a plentiful supply of eggs since 2015 (Credit: Alamy)
In theory, the scheme seems like a good idea, especially in parts of the world where eggs are either in shortage or very expensive. In California or New York, for example, a dozen eggs cost around $9 (£7). As some chicken breeds can lay up to 300 eggs every year, one chicken could lay up to $225 (£178) worth of eggs each year.
In practice though, Paul Behrens, a professor at the University of Oxford focusing on food systems, says there are some hurdles in the way: “I’m sure it could be done in the UK but I’m not sure it’s a good idea,” he says. “Bird flu is an ever-present worry. Current regulations mean you have to keep birds in fenced areas or indoors – this may again be a problem for animal welfare, or even disease spread if people don’t do this.”
The idea wouldn’t work well in the US either, says Mark Bomford, director of Yale University’s sustainable food programme. “I love chickens, but I don’t love the sound of this, especially in the US,” Bomford says.
The US is currently experiencing an egg shortage due to an outbreak of bird flu – and as a result egg prices have skyrocketed 36% compared to 2023 – but handing out free chickens would not be an “appropriate” response, Bomford says.
“Economically, steep inflation for a basic grocery item like eggs hurts the poor far more than it hurts the rich. To care for chickens you need feed, water, housing, space and free time,” he says. “Most people with lower incomes don’t have access to these things. By the time you have factored in all these costs, chickens are rarely ‘free’ and few people realise any net cost savings on eggs.”
One couple, however, did come up with a unique solution – renting chickens. Christine and Brian Templeton of Rent The Chicken in New Hampshire provide hens, feed and support for six months, allowing customers to collect fresh eggs at home. Business, the couple reports, is booming.
It’s important to temper egg expectations though, warns Behrens – industrial birds lay far more eggs than a home-kept healthy bird would. “Common and modern egg-laying birds are often in huge pain their entire lives, partly due to their genetics which are centred on providing as much ‘output’ as possible,” he says. “If you use older breeds and allow them to live a long, healthy life then you can avoid many of the most egregious animal welfare issues.”
“But people should then understand the tradeoff and expectations around that, you are having a much healthier bird in return for fewer eggs,” he says.
And from a food waste perspective, the ideal thing is to simply not waste the food in the first place – some researchers believe that composting can actually increase food waste.
“They think ‘oh, it’s okay as we compost’,” says Behrens. “Which is better than nothing but much worse than not wasting things in the first place. It could be even worse with chickens because you are getting eggs from them. People might waste even more than if they composted.”
But one unexpected benefit that was observed in Colmar – that had nothing to do with eggs or food waste – was the community the chickens created. Residents would bond over raising the chickens and would work with neighbours to care for the chickens when they went on holiday. “Residents have welcomed this operation since its launch,” says Straumann. “And that’s why all the municipalities in Colmar still participate in our programme today.”
– Lucy Sherriff
(BBC News)
You may like
FEATURES
JVP-NPP should learn difference between “marine research” & “surveillance”
Published
3 days agoon
June 21, 2025By
editor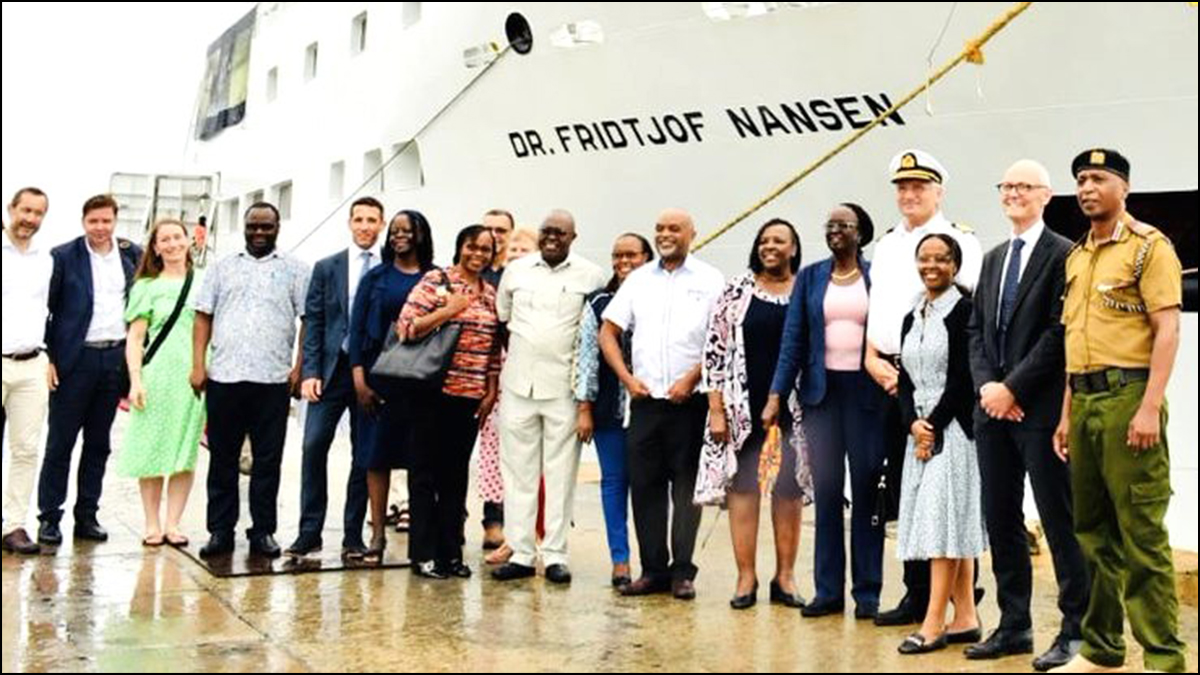

There’s now an apparent stand-off between the UN FAO and the Foreign Affairs Minister Vijitha Herath on the request made by the FAO to have permission for the UN flagged “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel to enter Sri Lankan waters. Minister Herath is on record saying the request would have to wait till the Committee on Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for foreign research vessels appointed by him and perhaps chaired by him too, complete their task in formulating the SOP. It was revealed, the SOP Committee is yet to be convened for the first time. With “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel waiting in Mauritius to set sail to Sri Lanka, numerous discussions the UN had with the Foreign Ministry (FM) since April has only reached the point, where the SL FM agreed to allow the ship to pick Bangladeshi “Scientists” from Colombo, but not get involved in any research in our waters.
res (SOP) for foreign research vessels appointed by him and perhaps chaired by him too, complete their task in formulating the SOP. It was revealed, the SOP Committee is yet to be convened for the first time. With “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” marine research vessel waiting in Mauritius to set sail to Sri Lanka, numerous discussions the UN had with the Foreign Ministry (FM) since April has only reached the point, where the SL FM agreed to allow the ship to pick Bangladeshi “Scientists” from Colombo, but not get involved in any research in our waters.
What’s this whole calamity over a FAO marine research ship requesting permission to enter Sri Lankan waters? Someone somewhere at the helm of the Foreign Ministry, or the Foreign Minister himself has wholly misinterpreted the issue of country owned research ships visiting Sri Lanka and the moratorium that was imposed by President Wickramasinghe barring foreign research ships.
Sri Lanka was pressured by India and the US to curtail if not stop Chinese research ships from docking in our ports in the past few years. Special concerns were over the 02 research ships “Yuan Wang 5” that docked at Hambantota in early 2022 during Gotabhaya’s presidency and “Shi Yan 6” in October 2023 at the Colombo port during Wickramasinghe’s presidency. It was said, these 02 research ships had the capacity for surveillance and monitoring the region. Under pressure especially from New Delhi, President Wickramasinghe decided to impose a one year moratorium on foreign research ships visiting Sri Lanka, effective from early January 2024.

The Wickramasinghe moratorium came to its end on 05 January 2025, as the JVP-NPP government did not extend it further. Reason to allow the moratorium to lapse in January, may have been on a strictly confidential agreement reached to have a separate bi-lateral agreement on defence, during President Anura Kumara’s maiden official visit to India in mid-December 2024. Defence had been an issue discussed with Indian authorities during President Anura Kumara’s Indian visit, wrote Dr. Samatha Mallempati of “Indian Council of World Affairs” in May 2025. A defence MoU would thus make the moratorium irrelevant thereafter. PM Modi was to visit Sri Lanka 04 months later in early April this year. One among the many MoUs the 02 governments signed during PM Modi’s visit was the first ever Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on “defence co-operation”.
India began working on a defence strategy for Indian Ocean Region (IOR) since the conclusion of Sri Lanka’s North-East civil war in 2009. New Delhi was very much concerned over President Rajapaksa’s post-war association with not only China, but with Pakistan too. Both with long time hostile border disputes with India. Contributing an article to “Stimson.org” on Pakistan-Sri Lanka relations in March 2021, two researchers on South & East Asian geo-politics Riaz Khokhar and Asma Khalid wrote, “In 2016, Pakistan signed a defense agreement with Sri Lanka to provide Colombo with eight JF-17 fighter aircrafts. Pakistani and Sri Lankan armies and naval forces have also regularly interacted through port calls, military and naval training and exercises, and defense workshops and seminars. In the recent high-level visit to Colombo, the Pakistani premier offered a USD $50 million credit line to Sri Lanka to further enhance defense and security partnerships.”
South Asian geo-politics did have new developments with post-war Sri Lanka compromising its economic needs with defence and national security in challenging the Tamil Diaspora canvassed US-Euro resolutions at UNHRC Sessions. Rajapaksa government was required to accept independent international investigations on war crimes and crimes against humanity, with many top military officers named. Pakistan stood with Sri Lanka, voting against all such resolutions at every UNHRC Session, while the Rajapaksa regime joined the Belt and Road Initiative of China, and was financially supported by China. Financial support that led to the popular adage “Sri Lankan type Chinese debt trap”.
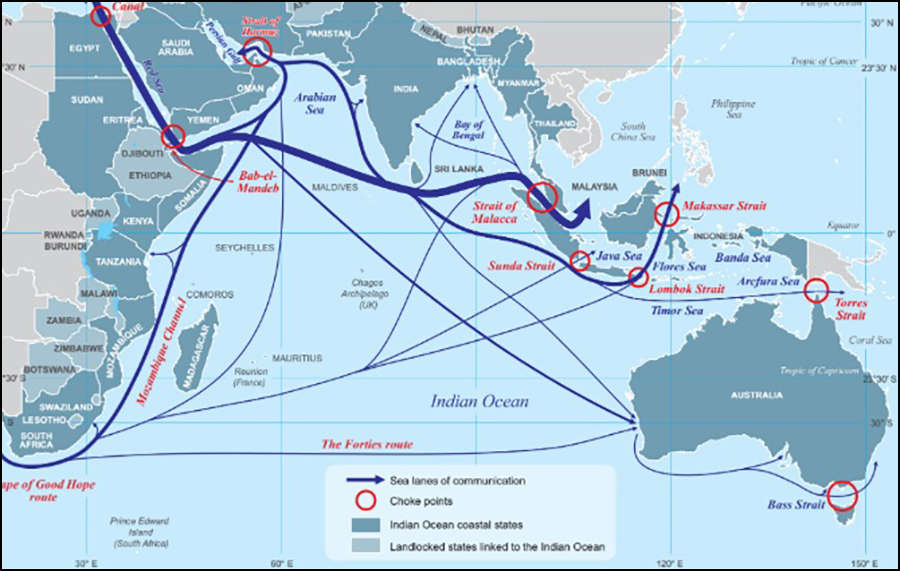
India has since been working towards establishing its dominance in the IOR keeping Sri Lanka as its focal point. Highlighting the geo-political importance of Sri Lanka, Dr. Samatha Mallempati wrote, “Since the region accounts for fifty percent of world maritime trade and seventy percent of global trade in oil and gas, there is a greater need to safeguard the sea lanes of communication. The increasing strategic significance of island states in the region therefore assumed importance. The island states such as Sri Lanka is looking to play a much bigger role by leveraging their geographical location.”
The perception in New Delhi that Sri Lanka is leveraging its geographical location to define geo-politics in the IOR, was what paved for the MoU on defence co-operation India signed with Sri Lanka, that for 05 years would provide India adequate space to influence Sri Lankan geo-politics in its favour. But the fact is, all these agreements and treaties are about IOR peace and stability and the influence “foreign countries” may have in it. The Sri Lankan moratorium was also about research ships of foreign countries, docking in our ports.
How would the UN flagged marine research ship “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” interfere in IOR stability and peace? The request to FAO for marine research in our waters had gone from the SL Government, never mind who led the government. FAO is focussed on sustainable fisheries management and this modern, fully equipped ship for marine research is used mainly in African and Indian Ocean waters in collaboration with NORAD to support developing countries with research based fisheries management. That perhaps was the only reason for the previous government to request the FAO to visit Sri Lankan waters. Mind you, that request for FAO to undertake marine research in our waters, went out while the moratorium on foreign research ships was fully effective.
Whatever the bureaucracy at the FM says, a seasoned politician like Vijitha Herath who had been in parliament for 25 years to date from year 2000, should know the difference between this UN flagged marine research ship and other research ships owned by individual countries. Anything flagged as “UN” is common property of 195 sovereign nation States who are UN members. This ignorance therefore very clearly exhibits the JVP/NPP leadership as the most intellectually timid leadership to have been voted to power since 1948 independence.
Kusal Perera
20 June, 2025
FEATURES
Adorable or just weird? How Labubu dolls conquered the world
Published
4 days agoon
June 20, 2025By
editor
Whether you reckon they are cute, ugly or just plain weird, chances are you have heard of the furry dolls that have become a global sensation – Labubu.
Born a monster, the elf-like creature from Chinese toy maker Pop Mart is now a viral purchase. And it has no dearth of celebrity advocates: Rihanna, Dua Lipa, Kim Kardashian and Blackpink’s Lisa. Ordinary folk are just as obsessed – from Shanghai to London, the long queues to snap up the doll have made headlines, sometimes descending into fights even.
“You get such a sense of achievement when you are able to get it among such fierce competition,” says avowed fan Fiona Zhang.
The world’s fascination with Labubu has almost tripled Pop Mart’s profits in the past year – and, according to some, even energised Chinese soft power, which has been bruised by the pandemic and a strained relationship with the West.
So, how did we get here?
What exactly is Labubu?
It’s a question that still bothers many – and even those who know the answer are not entirely sure they can explain the craze.
Labubu is both a fictional character and a brand. The word itself doesn’t mean anything. It’s the name of a character in “The Monsters” toy series created by Hong Kong-born artist Kasing Lung.
The vinyl faces are attached to plush bodies, and come with a signature look – pointy ears, big eyes and a mischievous grin showing exactly nine teeth. A curious yet divided internet can’t seem to decide if they are adorable or bizarre.
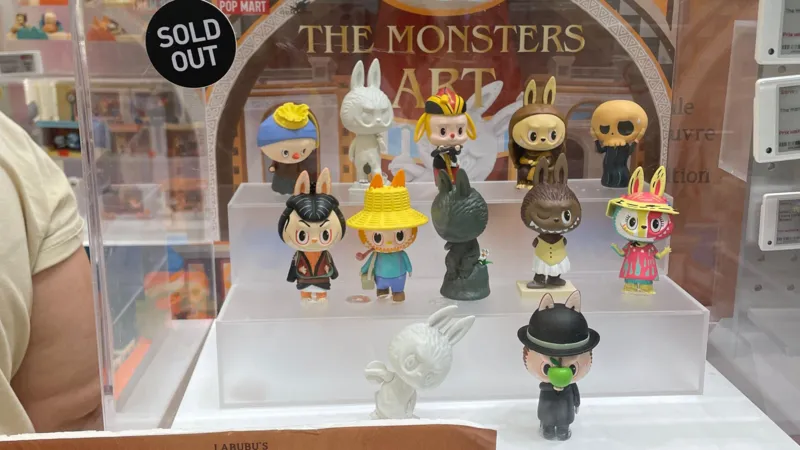

The Labubu universe includes other characters that have inspired their own dolls
According to its retailer’s official website, Labubu is “kind-hearted and always wants to help, but often accidentally achieves the opposite”.
The Labubu dolls have appeared in several series of “The Monsters”, such as “Big into Energy”, “Have a Seat”, “Exciting Macaron” and “Fall in Wild”.
The Labubu brand also has other characters from its universe, which have inspired their own popular dolls – such as the tribe’s leader Zimomo, her boyfriend Tycoco and her friend Mokoko.
To the untrained eye, some of these dolls are hard to distinguish from one another. The connoisseurs would know but Labubu’s fame has certainly rubbed off, with other specimens in the family also flying off the shelves.
Who sells Labubu?
A major part of Pop Mart’s sales were so-called blind boxes – where customers only found out what they had bought when they opened the package – for some years when they tied up with Kasing Lung for the rights to Labubu.
That was 2019, nearly a decade after entrepreneur Wang Ning opened Pop Mart as a variety store, similar to a pound shop, in Beijing. When the blind boxes became a success, Pop Mart launched the first series in 2016, selling Molly dolls – child-like figurines created by Hong Kong artist Kenny Wong.

Pop Mart first opened as a variety store in Beijing in 2010
But it was the Labubu sales that fuelled Pop Mart’s growth and in December 2020, it began selling shares on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Those shares have soared by more than 500% in the last year.
Pop Mart itself has now become a major retailer. It operates more than 2,000 vending machines, or “roboshops”, around the world. And you can now buy Labubu dolls in stores, physical or virtual, in more than 30 countries, from the US and UK to Australia and Singapore, although many of them have recently paused sales due to overwhelming demand. Sales from outside mainland China contributed to nearly 40% of its total revenue in 2024.
In a sign of just how popular Labubus have become, Chinese customs officials said this week that they had seized more than 70,000 fake dolls in recent days.
The demand did not rise overnight though. It actually took a few years for the elfin monsters to break into the mainstream.
How did Labubu go global?
Before the world discovered Labubu, their fame was limited to China. They started to become a hit just as the country emerged from the pandemic in late 2022, according to Ashley Dudarenok, founder of China-focused research firm ChoZan.
“Post-pandemic, a lot of people in China felt that they wanted to emotionally escape… and Labubu was a very charming but chaotic character,” she says. “It embodied that anti-perfectionism.”
The Chinese internet, which is huge and competitive, produces plenty of viral trends that don’t go global. But this one did and its popularity quickly spread to neighbouring South East Asia.
Fiona, who lives in Canada, says she first heard about Labubu from Filipino friends in 2023. That’s when she started buying them – she says she finds them cute, but their increasing popularity is a major draw: “The more popular it gets the more I want it.
“My husband doesn’t understand why me, someone in their 30s, would be so fixated on something like this, like caring about which colour to get.”

Labubu pendants are the most coveted
It helps that it’s also affordable, she adds. Although surging demand has pushed up prices on the second-hand market, Fiona says the original price, which ranged from 25 Canadian dollars ($18; £14) to 70 Canadian dollars for most Labubu dolls, was “acceptable” to most people she knows.
“That’s pretty much how much a bag accessory would cost anyway these days, most people would be able to afford it,” she says.
Labubu’s popularity soared in April 2024, when Thai-born K-pop superstar Lisa began posting photos on Instagram with various Labubu dolls. And then, other global celebrities turned the dolls into an international phenomenon this year.
Singer Rihanna was photographed with a Labubu toy clipped to her Louis Vuitton bag in February. Influencer Kim Kardashian shared her collection of 10 Labubu dolls with her Instagram following in April. And in May, former England football captain Sir David Beckham also took to Instagram with a photo of a Labubu, given to him by his daughter.
Now the dolls feel ubiquitous, regularly spotted not just online but also on friends, colleagues or passers-by.
What’s behind the Labubu obsession?
Put simply, we don’t know. Like most viral trends, Labubu’s appeal is hard to explain – the result of timing, taste and the randomness that is the internet.
Beijing is certainly happy with the outcome. State news agency Xinhua says Labubu “shows the appeal of Chinese creativity, quality and culture in a language the world can understand”, while giving everyone the chance to see “cool China”.
Xinhua has other examples that show “Chinese cultural IP is going global”: the video game Black Myth: Wukong and the hit animated film Nezha.

A Pop Mart store in Shanghai
Some analysts seem surprised that Chinese companies – from EV makers and AI developers to retailers – are so successful despite Western unease over Beijing’s ambitions.
“BYD, DeepSeek, all of these companies have one very interesting thing in common, including Labubu,” Chris Pereira, founder and chief executive of consultancy firm iMpact, told BBC News.
“They’re so good that no one cares they’re from China. You can’t ignore them.”
Meanwhile, Labubu continue to rack up social media followers with millions watching new owners unbox their prized purchase. One of the most popular videos, posted in December, shows curious US airport security staff huddling around a traveller’s unopened Labubu box to figure out which doll is inside.
That element of surprise is a big part of the appeal, says Desmond Tan, a longtime collector, as he walks around a Pop Mart store in Singapore vigorously shaking blind boxes before deciding which one to buy. This is a common sight in Pop Mart.
Desmond collects “chaser” characters, special editions from Pop Mart’s various toy series, which include Labubu. On average, Desmond says, he finds a chaser in one out of every 10 boxes he buys. It’s a good strike rate, he claims, compared to the typical odds: one in 100.
“Being able to get the chaser from shaking the box, learning how to feel the difference…,” is deeply satisfying for him.
“If I can get it in just one or two tries, I’m very happy!”
– Fan Wang, Adam Hancock
(BBC News)


Remember listening to a young lady TV Anchor in a private TV channel a few months ago, demanding from an Opposition MP, what threats he is referring to as “threats to national security”. On her own definition, she was quite certain there are “no threats to national security” as claimed by the Opposition. “Its past midnight when I go home…. after these programmes” she said on camera. “I have never felt any threat to me” she added. The opposition argument was, heavy increase in “shootings” during the past few months in most parts of the country and an increase in deaths due to such shootings, would bring about a threat to “National Security” if not controlled immediately.
But what is “National Security?”

The concept of “national security” evolved over many decades ago with assumed “external threats” to a nation and its people. During the past two plus decades, especially after the New York 9/11 terrorist attack, the concept of national security has been broadened beyond “nations” with intensive intelligence gathering networks. Ethnic and religious conflicts, border clashes and environmental degradation have been added since. The most recent Indo-Pak armed conflict, is one that is spoken of as a “national threat” to India among “Shiv Sena and Hindutva” groups.
We in Sri Lanka, did have remotely manipulated threats to our national security, first in early 1980’s when Indira Gandhi was Prime Minister in neighbouring India. Her perception of Jayawardene presidency as heavily weighted towards US, was what compelled her to intervene in our politics. In his book “Assignment Colombo” the Indian High Commissioner in Colombo J.N. Dixit wrote, “The first step that Mrs. Gandhi took was to give support to Sri Lankan Tamil parties and Tamil militant groups from 1980 onwards, details of which have been mentioned in a number of articles and books over the last 09 years. There is no need for me to repeat them”. (p/15)
As said, details given in many other writings confirm PM Indira Gandhi provided Sri Lankan armed Tamil groups with funds, military training and arms. In 1997, visiting Dehradun that borders Himalayas, I had a wholly unexpected meeting with a social activist very close to the Gandhi family. He took me to the “Rashtriya Indian Military College” in Garhi Cantt, where a select group of LTTE cadres had been trained to use “RPGs” and mortars. I was shown a massive rock in the hills, not too far away from the military college and told, mortars were fired at that rock during training.
Then Tamil Nadu (TN) Chief Minister, Sri Lankan born M.G. Ramachandran, popularly known in Tamil cinema as MGR, provided special accommodation to most Tamil armed group leaders and is said to have funded the LTTE nurturing a special fancy towards Prabhakaran. All that certainly was collective Indian manipulations in undermining our national security.

The next came in 1987 June. Then State Minister of Defence Lalith Athulathmudali a hardliner in Indo-Sri Lanka relations, endorsed a military offensive in March 1987 to take over Jaffna peninsula. Towards end May, the state military entered Jaffna peninsula and was pushing the LTTE towards Wadamarachchi. New Delhi hastened to inform the Colombo government, they want the “Wadamarachchi offensive” stopped immediately, to avoid a situation of mass hunger in the peninsula. Food not used as a “weapon of war”, Athulathmudali was determined to take-over whole of Jaffna peninsula in less than 02 weeks and was in no mood to halt the military offensive.
Yet Tamil Nadu convinced PM Rajiv Gandhi to decide on a flotilla of naval boats to deliver food to Jaffna. When Sri Lankan navy stopped them from entering SL waters and forced them to return to Rameswaran on June 03, India had decided on the ill-famed “air drop” on Jaffna, violating Sri Lankan airspace. On 04 June the airdrop of food parcels was carried out with SL High Commissioner in New Delhi Bernard Thilakaratne informed of the air drop about an hour before. Next day the Indian media carried the news of Indian Air force “successfully” completing “Operation Poomalai” by dropping food parcels on Jaffna that brought the Wadamarachchi offensive to a stop.
The last such threat on Sri Lankan national security was when PM Rajiv Gandhi in July 1987 almost coerced President Jayawardene to accept his government’s answer to the Sri Lankan Tamil armed conflict. The Indo-Sri Lanka Accord was signed in Colombo in July 1987 that led to Indian Peace Keeping Forces (IPKF) taking over security of North-East and formation of elected Provincial Councils with devolved power. In Sinhala South, opposing the PCs and the IPKF presence, the JVP unleashed a terror campaign leading to complete mayhem.
All that being history, since President Rajapaksa declared the war as “victoriously concluded” on 19 May, 2009 with the LTTE and its entire leadership eliminated, Modi’s India has become a strong ally of Sri Lanka in its efforts to tide over the recent economic crisis. There remained no other external factor that can be assumed as an imminent threat to Sri Lanka’s national security.
What then is the Opposition assuming as a possible threat to our national security with increased shootings and deaths during the past few months? Unless these underworld groups are bought over by an “external agency” in the future, for now, they are only a threat to social stability and peace, and not “national security”. They act on their own agenda, nevertheless creating an uncertainty about citizen’s safety and security to life. It is therefore about how efficient the government is, in policing society, ensuring law and order for all and one.
NPP Foreign Policy & Genocide
If at all, what could in the future be a threat to our national security is the present NPP government’s pro-US foreign policy that accommodates Israel as a “peaceful” non-aggressive State, ignoring the genocidal war against Palestine. But on the ground, with mass recruitments of Israeli youth for the ongoing military offensives against Palestine since October 2023, Israeli government needs labour for their community based farming and for quick reconstruction of damaged buildings due to Hamas rocket fire.
Since Gotabhaya Rajapaksa as Secretary to the Ministry of Defence opened up links for Sri Lankan migrant employment in Israel, 02 MoUs signed between the two governments have in 2020 provided jobs for home stay female caregivers and again in 2023 for agriculture labour, subsequently extended for construction work as well. This year during the first 03 months, nearly 2,000 Sri Lankans have left to Israel as construction workers. In mid May this year, another 447 Sri Lankans were ready to leave according to Sri Lanka Bureau of Foreign Employment (SLBFE). (https://www.slbfe.lk/slbfe-news/447-sri-lankans-to-begin-employment-in-israels-construction-sector/)
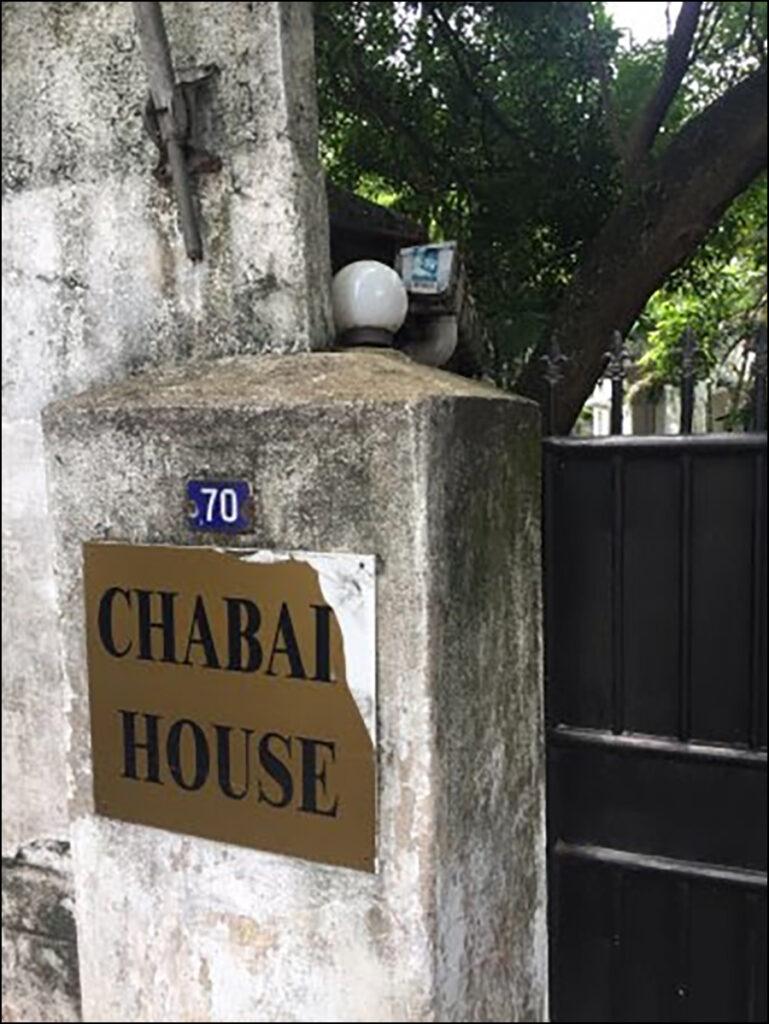

Added is the space provided by this NPP government for Israeli “tourists” to basically live here in Sri Lanka, with their own abodes and establishing cultural centres called “Chabad Houses”. It is rather puzzling how the NPP government could allow Israeli “tourists” to establish their cultural centres the government too accept as illegal, while providing armed police security for their safety. Presumably after a protest on the opposite pavement in front of the Chabad House in Kollupitiya on 09 May, a hurried announcement made by the Police Media Division on 11 May (2025) says, Israelis staying in Sri Lanka who have established Chabad Houses in some police divisions for their convenience, have been provided adequate security by those police divisions, due to threats to Chabad Houses. The police media division also says, if any foreign nationals staying in Sri Lanka needs security, SL Police would provide adequate security after an assessment on threats.
This NPP government’s foreign policy that officially provides SL labour for warring Israel and allows Israelis to “stay” in Sri Laka with State security, may in the future open Sri Lanka for “external” anti-Israeli threats as was discussed in many social forums over alleged ISIS links during the 2019 April Easter Sunday attacks that left 253 fatalities.
This possibility of destabilising Sri Lanka by external anti-Israeli agents, can only be counted by a principled change in foreign policy of the NPP government. With strong US support to stay within the IMF programme and with no alternate thinking, this government’s foreign policy can only be positively changed by rational social interventions by the Opposition that to date is totally absent. Sadly in Colombo, even the generally accepted educated, professional middleclass perception is wholly flawed. They claim they oppose genocide and stand in solidarity with Palestine, but have no demands for this NPP government to honour at least a viable ceasefire. No demand the NPP government should stop providing SL labour to Israel, heavily engaged in a brutal a war that to date has left over 55,000 Palestinians killed counting around 70 percent children and women, 180 journalists and over 224 humanitarian aid workers including 179 that worked for UN Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA).
If dollar remittances are all what matters to the NPP government, this NPP foreign policy of accommodating Israel, whose PM Benjamin Netanyahu and his former Defence Minister Yoav Gallant have arrest warrants issued by the International Criminal Court (ICC) for war crimes and crimes against humanity in Gaza, may invite threats to our national security, neither the NPP government nor the Opposition is willing to pay attention to.
– Kusal Perera

NPP secures control of 200 LG bodies

10 J’pura students unnecessarily charged for hostel damages – CoPE